Mobile apps are no longer static experiences. As artificial intelligence continues to advance, apps are becoming smarter and more intuitive.
Adaptive UI, powered by AI, is revolutionizing how mobile apps interact with users by dynamically adjusting interfaces based on behavior, preferences, and context.
Imagine opening your favorite shopping app and seeing personalized recommendations, rearranged menus based on your past behavior, and features that anticipate your needs before you even search for them. This is the power of an adaptive UI, and it’s reshaping how we engage with digital experiences.
According to a study, adaptive user interfaces also boost user engagement rates by up to 31% and user task completion rates by 22%.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI-driven adaptive UIs work, the key benefits they offer, and real-world examples of apps that are already using this technology to create highly personalized user experiences.
What is an Adaptive UI?
(Source: Dribbble/ Outcrowd)
An adaptive UI is a user interface that changes dynamically to fit the needs of each user. Instead of offering a one-size-fits-all experience, an adaptive UI evolves based on user behavior, preferences, device type, and real-time context.
Traditional mobile apps rely on fixed navigation menus, layouts, and user flows. Adaptive UI, on the other hand, adjusts elements like button placements, font sizes, color schemes, and content recommendations based on individual interactions.
This ensures that every user gets a personalized and optimized experience without manually adjusting settings.
For example, a fitness app with an adaptive UI might prioritize workout suggestions based on a user’s past activity patterns, showing cardio exercises for someone who runs frequently while highlighting strength training for someone who lifts weights.
How AI Powers Adaptive UI
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in creating adaptive UI experiences. By analyzing large amounts of data, AI can identify patterns, predict user behavior, and make real-time adjustments to an app’s interface. Here’s how AI makes it happen:
Machine Learning for User Behavior Analysis
Machine learning allows apps to analyze how users interact with different UI elements. It tracks which buttons are clicked most often, which features are ignored, and how users navigate the app. Over time, AI can detect trends and adjust the UI accordingly.
For example, if a music app notices that a user frequently listens to calming playlists at night, it might rearrange the home screen to feature sleep-friendly music recommendations in the evening.
Predictive Personalization
AI can predict user needs before they even express them. This is done by analyzing past behaviors, preferences, and contextual factors like time of day, location, and device usage habits.
For instance, a travel app might automatically suggest nearby restaurants around lunchtime based on the user’s previous dining preferences and current location.
Similarly, a news app might prioritize articles from topics a user frequently reads, adjusting the homepage to display relevant stories first.
Natural Language Processing for Smarter Interfaces
Many adaptive UIs integrate natural language processing (NLP) to improve user interactions. AI-driven chatbots, voice assistants, and smart search functions help users navigate apps more efficiently by understanding conversational input.
For example, a shopping app with an AI-powered search bar can suggest product categories, autofill queries based on browsing history, and refine search results based on previous purchases.
Context-Aware Adjustments
Adaptive UI can respond to real-time factors like device type, screen size, and accessibility settings. This ensures that the interface is optimized for each unique user environment.
A great example of this is in ride-sharing apps, where the UI changes based on location. If a user is at an airport, the app might highlight ride options specifically for airport pickups, while a user in a city center might see nearby bike rentals instead.
Real-World Examples of Adaptive UI in Action
Many popular apps are already leveraging AI to create adaptive UIs. Here are some standout examples:
Spotify
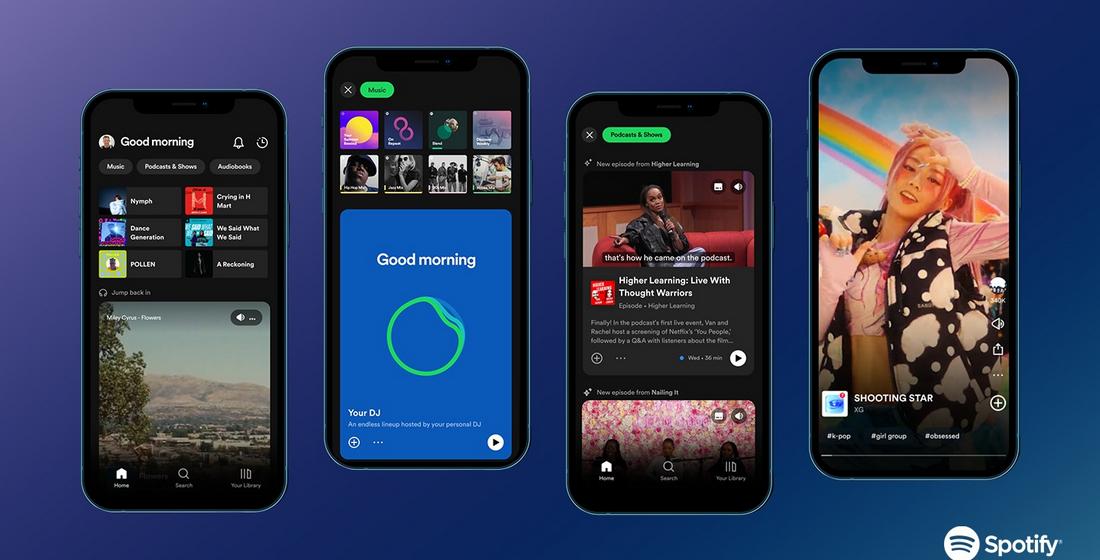
Spotify uses AI to analyze listening habits and adjust the UI based on user preferences. Personalized playlists like “Discover Weekly”” and “Daily Mix” are placed prominently on the home screen, ensuring that users always see relevant music recommendations.
Google Maps
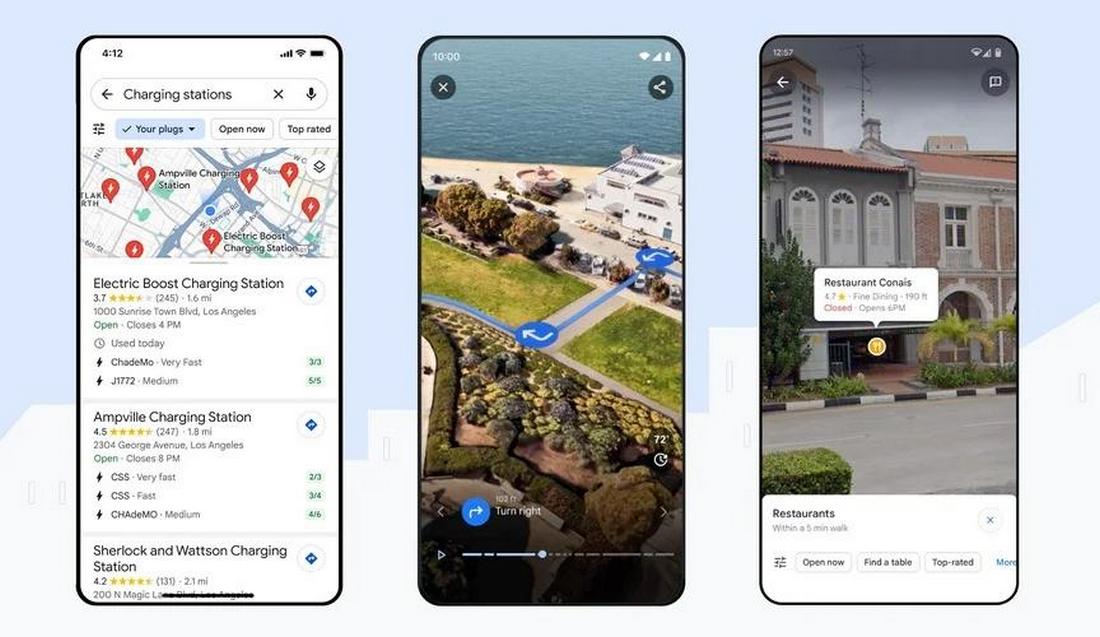
Google Maps dynamically changes its UI based on user behavior and location. If a user frequently commutes at a certain time, the app prioritizes traffic updates and commute shortcuts during those hours. It also adapts search suggestions based on the user’s location, showing nearby gas stations, restaurants, or transit stops.
Amazon Shopping App
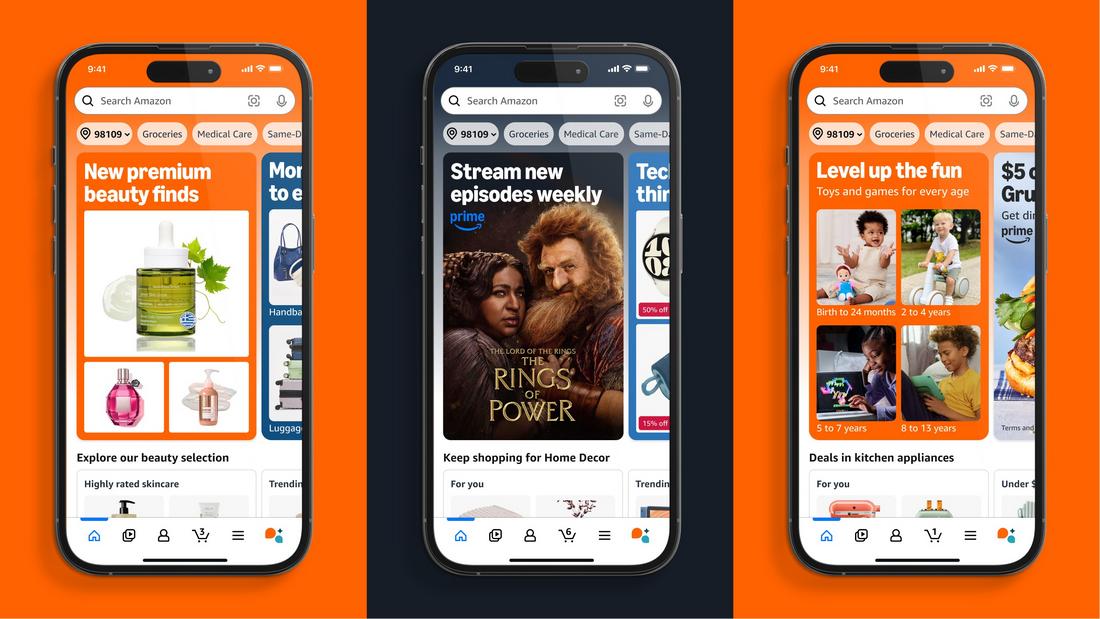
Amazon’s mobile app personalizes the shopping experience by rearranging product categories and recommendations based on browsing history, purchase behavior, and seasonal trends. Users see promotions and deals tailored to their interests, making the app more engaging and conversion-friendly.
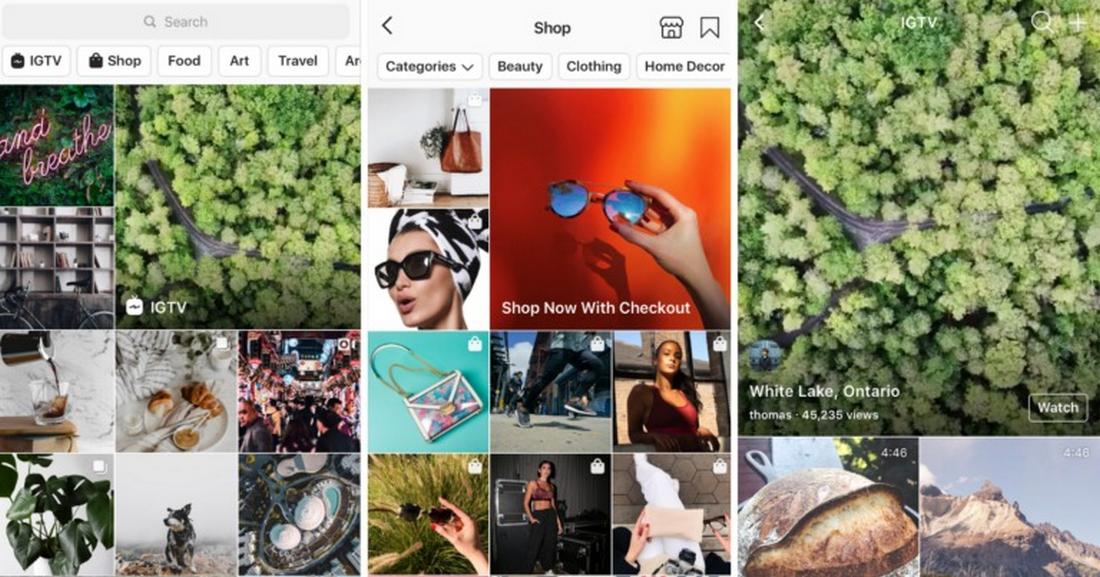
Instagram’s Explore page is a perfect example of an adaptive UI. The content shown in the explore tab is based on user engagement patterns, ensuring that each user sees posts, reels, and accounts aligned with their interests. The algorithm continuously updates the UI to reflect changing preferences.
Benefits of Adaptive UI in Mobile Apps
1. Enhanced User Experience
An adaptive UI makes apps easier to navigate by presenting users with the most relevant options. When an interface adapts to a user’s habits, it reduces friction and makes interactions feel more natural. Users don’t have to search for frequently used features—they are automatically surfaced for them.
2. Increased Engagement and Retention
Users are more likely to stay engaged with an app that feels tailored to their needs. By offering personalized recommendations, content, and layouts, adaptive UIs keep users coming back. The more relevant an experience feels, the higher the chances of user retention.
For example, video streaming apps like Netflix and YouTube use adaptive UIs to recommend content based on watch history. This level of personalization keeps users engaged by ensuring they always have something relevant to watch.
3. Improved Accessibility
AI-driven UI adjustments can improve accessibility by tailoring interfaces to users with different needs. This includes larger text for visually impaired users, voice-assisted navigation for those with mobility challenges, and high-contrast modes for better readability.
For example, smartphone operating systems like iOS and Android use adaptive UI to adjust font sizes and button placements based on accessibility settings, making apps more inclusive.
4. More Efficient Workflows
In productivity apps, an adaptive UI can streamline workflows by bringing frequently used tools to the forefront. A project management app, for instance, might prioritize showing a user’s most active projects or tasks that need immediate attention, eliminating unnecessary steps.
In Conclusion
Adaptive UI is reshaping mobile app experiences by making them more personalized, intuitive, and user-friendly. By leveraging AI-driven insights, apps can dynamically adjust layouts, recommendations, and interactions to better serve each user.
As AI continues to evolve, adaptive UI will become even more sophisticated. Future advancements may include emotion recognition technology that adjusts UI elements based on user mood, or gesture-based interfaces that respond to subtle movements.
Soon, AI-driven UI design could extend beyond web and mobile apps into wearables, smart home devices, and even augmented reality interfaces.
