
If you find yourself increasingly turning to large language models (LLMs) like Google Gemini or ChatGPT when searching for information online, you’re not alone.
Many people treat traditional search and LLMs as a binary choice — one or the other. But in reality, search engines and generative search are experiential competitors, not direct ones. They do very different things, as the table below shows:
| Search Engines | Generative Search |
| Competitor in function | Competitor in experience |
| Built for links | Built for answers |
| Owns web traffic | Owns user trust |
Think of generative search as an analyst
As a marketer, it’s helpful to think of generative search products as unbiased analysts engaging audiences of diverse personas. These tools aim to understand each persona’s intent, analyze relevant data, and personalize results based on user input.
Because search and generative tools work differently, marketers must rethink digital visibility and shift from an SEO mindset to a generative search optimization mindset.
An SEO mindset sounds like: “If we target keywords X with content Y and build Z backlinks, we should rank on page one and drive conversions.”
The generative search mindset is broader: “If we establish ourselves as the authoritative source on topics related to our products and services, we increase the likelihood of being cited and recommended by AI systems.”
The shift to LLMs is real
LLMs are rapidly changing the landscape of digital visibility.
Semrush (parent company of MarTech publisher Third Door Media) recently studied the impact of AI search on SEO. The analysis predicts that AI search engagement will increase as the technology becomes more familiar. As user habits evolve, many clicks will shift from traditional to AI search — or disappear altogether.
Understanding AI brand relevance
Traditional digital marketing has centered on conversion optimization and keyword targeting. Effective AI brand relevance, however, is rooted in:
- Authority building: Becoming a definitive source on topics relevant to your brand.
- Information architecture: Structuring content so AI systems can confidently interpret it.
- Multi-dimensional presence: Publishing diverse, high-quality content across platforms.
- Training beyond guidelines: Inserting brand data in less obvious but contextually appropriate locations to aid learning.
- Cross-ecosystem consistency: Maintaining coherent messaging across digital properties.
The fragmented LLM landscape
Unlike Google’s dominance in traditional search, no LLM has emerged as the clear leader. And each platform behaves differently.
- Google’s Generative Search is built on traditional search, promoting content through its E-E-A-T framework: experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness.
- ChatGPT’s search often bypasses top-ranked results in favor of deeper content.
Visibility varies by platform
Google Overviews and Gemini heavily index Quora, Reddit, and YouTube. Content on these platforms may enhance AI visibility.
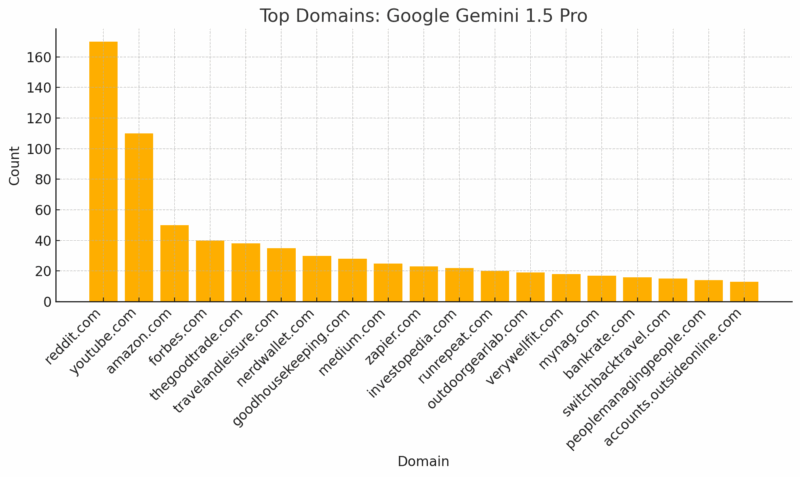
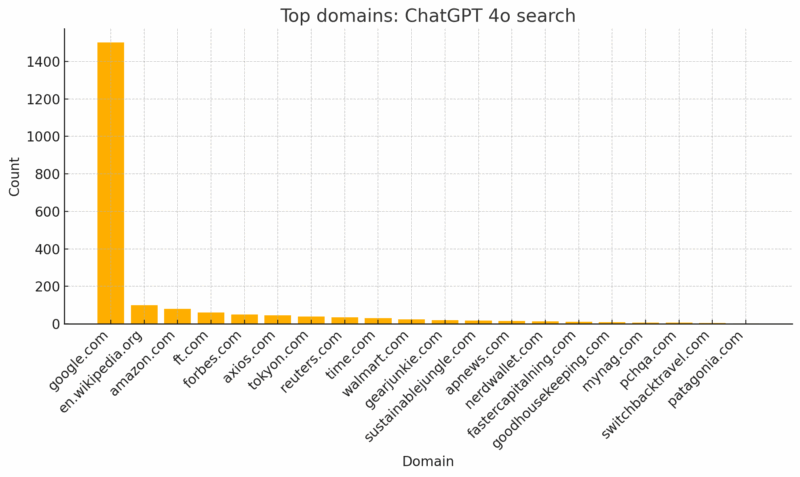
ChatGPT relies on Google.com more than any other site. A broad and deep keyword strategy supports visibility there.
Measuring your LLM visibility
Like SEO, LLM visibility can and should be measured. This allows marketers to demonstrate progress and justify investment in generative optimization.
LLM visibility is a probabilistic measure of how often your brand appears in AI responses to relevant prompts. It combines:
- Persona: Who is asking?
- Prompt: What are they asking?
By pairing multiple personas with prompts, you simulate conversations. The presence of your brand in those conversations determines visibility. Because each LLM behaves differently, you need cross-platform visibility scoring.
Formulas to know:
- Personas × Prompts × LLMs = Conversations
- Conversations × Brand Mentions = LLM Visibility
Conversation visibility factor
At the conversation level, you can use Gumshoe.ai to get a competitive ranking for each brand mentioned in the response. Using this information, you can generate a conversation visibility factor for each prompt through this formula:
(Brand Visibility % / Brand Rank) x Link Visibility = Visibility Factor
Link Visibility is a preselected value between 0 and 1 based on the nature of the prompt. LLMs are less likely to display related links for general knowledge prompts. Prompts that are more specific and require more complex responses are more likely to include links to mentioned products and services.
| Prompt | Visibility % | Brand Rank | Link Visibility (0-1) | Visibility Factor |
| What is SEO? | 57% | 6 | .01 | 0.95% |
| What are the best SEO competitor analysis tools? | 76% | 1 | .09 | 68% |
You can use the Visibility Factor to measure the impact of optimizations at the prompt level. By clustering prompts by level of specificity, you can measure your authority at each level. You can use this to monitor and adjust your target prompts to find the ideal mix of prompt performance.
Core optimization strategies
The good news: SEO teams are well-positioned to succeed in the era of generative optimization, or AIO (AI optimization).
Due to their reach, Google and ChatGPT remain key priorities. Because ChatGPT heavily indexes Google, optimizing for Google can help with visibility on both.
There are two categories of content to optimize:
1. Human-viewable content. This is content designed for human readers and includes:
- E-E-A-T optimization: Essential for feeding Google AI Overviews.
- Clear content structure: Use headers, bullet points, comparison tables, and FAQs to make information scannable for LLMs.
- Precise language: Match terms to likely prompt intent.
- Comparative content: LLMs often respond to questions like “Which is better?”—make sure your content includes comparisons.
- Unique insights: Highlight exclusive advice, brand values, and original research.
2. LLM-optimized content. This supports LLM comprehension:
- Markdown publishing: Use semantically clean markdown files to improve crawlability.
- Reinforcement Training: A more advanced method for embedding brand signals into LLMs through statistical learning.
Reinforcement training explained
LLMs build statistical models from large data sets. You can influence their outputs by feeding them relevant, structured data.
Steps:
- Identify high-value proof points from customer records.
- Remove PII and sensitive data.
- Create large, structured datasets formatted for machine learning.
- Link them from relevant markdown pages.
- Track changes in LLM visibility and site traffic.
- Update quarterly.
LLMs reward structured, high-volume datasets that enhance their ability to generate relevant responses. It will become morecriticalt as AI agents capable of completing tasks emerge in late 2025 and beyond.
Explaining LLMs and AIO to leadership
Executives may not need deep technical details but must understand the strategic impact. Here’s how to frame it:
- Define the issue: Use internal data to show how LLMs affect traffic, conversions and visibility.
- Quantify the threat: Project future losses if nothing is done.
- Benchmark today: Show current LLM visibility and set future targets.
- Show the plan: Outline tactics, timelines, KPIs and required resources.
The post How to get started with AI optimization (and explain it to your leadership) appeared first on MarTech.
